,文章长度在1000字左右。
html
Dew Point Calculation Methods and Formulas
The dew point is a crucial meteorological parameter that indicates the temperature at which air becomes saturated with water vapor, leading to condensation. Understanding how to calculate the dew point is essential for weather forecasting, HVAC systems, and industrial processes. This article explores the various methods and formulas used to determine the dew point.
What Is Dew Point?
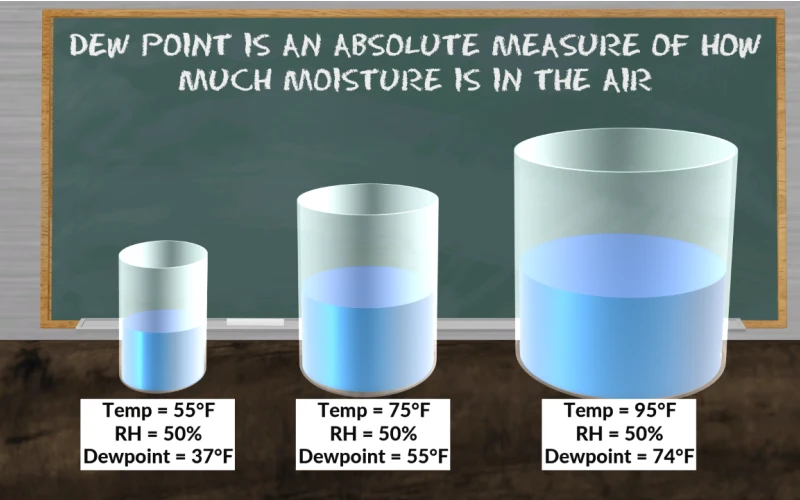
Dew point is the temperature at which air must be cooled to become saturated with water vapor, assuming constant pressure and water content. When the air temperature drops to the dew point, water vapor condenses into liquid water, forming dew, fog, or clouds. The higher the dew point, the more moisture the air contains.
Basic Dew Point Calculation
The simplest method to estimate the dew point involves using the Magnus formula, which relates the dew point temperature (Td) to the actual air temperature (T) and relative humidity (RH). The formula is:
Td = (b × α(T, RH)) / (a – α(T, RH))
Where:
- α(T, RH) = (a × T) / (b + T) + ln(RH/100)
- a = 17.27 (constant for water)
- b = 237.7 °C (constant for water)
- T = air temperature in °C
- RH = relative humidity in %
Improved Magnus Formula
An enhanced version of the Magnus formula provides greater accuracy, especially for temperatures below 0°C. The improved formula is:
Td = (c × α(T, RH)) / (d – α(T, RH))
Where:
- α(T, RH) = (d × T) / (c + T) + ln(RH/100)
- c = 17.62 (constant for improved accuracy)
- d = 243.12 °C (constant for improved accuracy)
Using Psychrometric Charts
Psychrometric charts are graphical tools that display the relationship between air temperature, humidity, and dew point. By knowing two of these parameters, the third can be determined by locating the intersection point on the chart. This method is widely used in HVAC and engineering applications.
Arden Buck Equation
For more precise calculations, the Arden Buck equation is often used. It accounts for variations in atmospheric pressure and provides accurate results across a wide temperature range:
Td = (c × ln(e / e0)) / (a – ln(e / e0))
Where:
- e = vapor pressure
- e0 = saturation vapor pressure
- a, b, c = empirical constants
Online Calculators and Software
Many online tools and software applications simplify dew point calculations by automating the formulas mentioned above. Users only need to input temperature and relative humidity values to obtain instant results. These tools are particularly useful for quick estimations in fieldwork or industrial settings.
Practical Applications of Dew Point
Keyword: how is dew point calculated
